3. IELTS Academic Writing Task 1: Ultra-Interactive Guide, Practice, and Model Answers – Waste Management Trends [2025]
-
July 29, 2025
![Unlock your highest IELTS Writing Task 1 band with this ultra-interactive tutorial! Featuring step-by-step strategies, a complex sample task with model answers, vocabulary and phrases breakdown, and instant practice quizzes—all based on the latest IELTS trends for 2025. Master waste management charts, expand your academic vocabulary, and boost your writing skills with LingExam’s expert guide. Perfect for serious IELTS candidates aiming for Band 7 and above! - IELTS Academic Writing Task 1: Ultra-Interactive Guide, Practice, and Model Answers – Waste Management Trends [2025] - LingExam Language Academy - Lingexam.com](https://lingexam.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Article-Thumbnail-38.jpg)
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1: Step-by-Step Band 9 Tutorial (LingExam | Ultra-Interactive)
Welcome! In this tutorial, you’ll master IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 for the following complex question type:
The charts below show the percentage of waste material recycled, landfilled, and incinerated in three European countries (Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom) in 2015 and 2025 (projected).
Follow each step below. Hover on any step to highlight and reveal advanced notes for Band 7+.
The charts below show the percentage of waste material recycled, landfilled, and incinerated in three European countries (Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom) in 2015 and 2025 (projected).
Follow each step below. Hover on any step to highlight and reveal advanced notes for Band 7+.
How to Answer IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 (Charts): 12 Essential Steps
1
Read the question carefully. Make sure you know exactly what is being shown. Identify the countries, the years, and the types of waste management. Always underline or mentally note all categories and time periods.
2
Scan both charts/images and spot all the main categories. Here, look for recycled, landfilled, and incinerated waste in Germany, Italy, and the UK, in both 2015 and 2025. Note which country leads or lags in each method.
3
Quickly identify the overall changes and contrasts. For example, does recycling increase everywhere? Does landfilling drop? Is there a method that remains stable? This gives you a roadmap for your report structure.
4
Write a high-level overview in your mind. For Band 7+, you need to summarise overall trends, not list all details. Use phrases like “Overall, recycling increased while landfilling decreased in all countries.”
5
Group the data meaningfully. For example, compare all countries’ recycling rates in both years, then all landfilling rates, etc. Grouping shows examiner you can compare, not just describe.
6
Make comparisons with precise language. “Germany recycled the highest percentage in both years, while Italy’s rates were lower but increased.” Use comparatives (higher, lower, more than, less than) and transitions (whereas, while, in contrast).
7
Always support your claims with data from the charts. For example, “Germany’s recycling rate increased from 62% in 2015 to 70% in 2025.” Avoid opinions or explanations for changes!
8
Don’t overload your overview paragraph with numbers. Give the big picture in your overview, and leave specific data for the following paragraphs.
9
Structure your writing into logical paragraphs. Usually, one for overall trends and one or two for details (e.g., recycling, landfilling, incineration, or by country). This helps coherence and progression.
10
Use synonyms and varied sentence structures. For example, “percentage,” “proportion,” “share,” “rate,” “accounted for.” This shows your lexical resource and improves your score.
11
Describe past data in past simple, future data with “is projected to,” “is expected to.” Use the passive for formality: “was recycled,” “is projected to be landfilled.”
12
Review for grammar, data accuracy, and full task coverage. Did you summarise, make comparisons, use data, and avoid personal opinions? Proofread for errors before moving on!
Band 9 Sample Plan & Example Notes
Overview Example: “Overall, all three countries are projected to increase the percentage of waste recycled by 2025, while landfilling is expected to decrease. Germany remains the leader in recycling both years.”
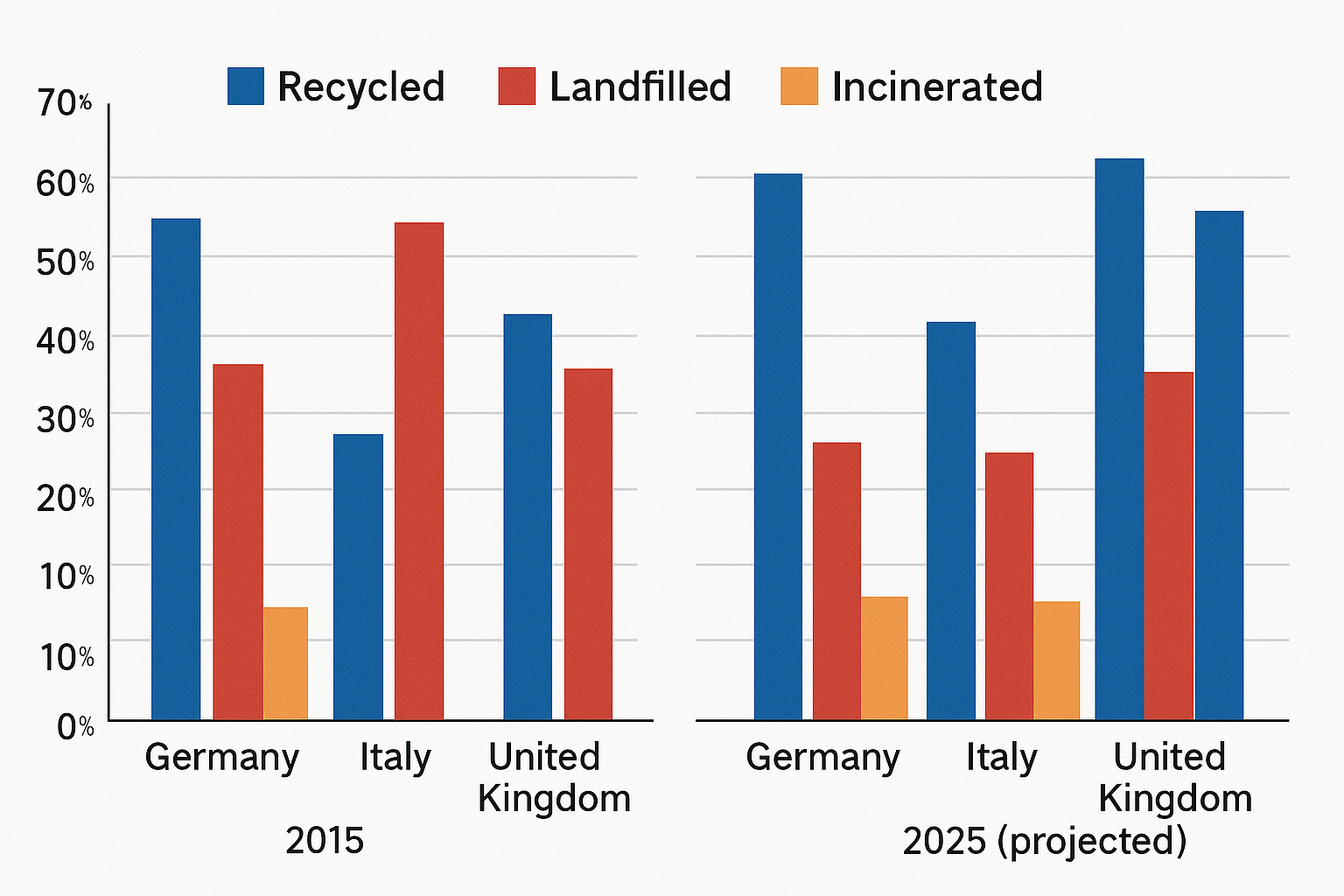
Grouping Example: “Recycling rates were highest in Germany (62% in 2015), increasing to 70% by 2025, while the UK saw a significant rise from 45% to 58%.”
Grouping Example: “Recycling rates were highest in Germany (62% in 2015), increasing to 70% by 2025, while the UK saw a significant rise from 45% to 58%.”
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
Task:
The charts below show the percentage of waste material recycled, landfilled, and incinerated in three European countries (Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom) in 2015 and 2025 (projected).
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Charts: Waste Management in Three European Countries (2015 & 2025)
Click the image to view full screen & zoom
 ×
×
Pinch/scroll to zoom – Tap/click anywhere to exit
Your Answer:
Tip: After writing, check your grammar, data, and make at least two clear comparisons between countries and between years!
Band 9 Model Answer & Step-by-Step Explanations
Review the full Band 9 sample answer and reveal step-by-step how each part achieves a high score. Expand each step for a deep explanation, and test yourself with interactive quiz questions!
1
Introduction:
(Show/Hide)
The two charts compare the percentage of waste materials that were recycled, landfilled, and incinerated in Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom in 2015 and projections for 2025.
Explanation:
This introduction paraphrases the question using synonyms and introduces all categories and time frames. A clear, accurate intro shows the examiner you fully understood the visuals and task. Avoid copying the prompt word-for-word and make sure to mention all countries, years, and waste management types.
This introduction paraphrases the question using synonyms and introduces all categories and time frames. A clear, accurate intro shows the examiner you fully understood the visuals and task. Avoid copying the prompt word-for-word and make sure to mention all countries, years, and waste management types.
2
Overview:
(Show/Hide)
Overall, all three countries are projected to increase the proportion of waste recycled by 2025, while landfilling is expected to decline. Germany remains the leader in recycling in both years.
Explanation:
A strong overview summarises the main trends, not details, for a Band 7+. The writer points out increases and decreases and makes a comparison between countries. No specific numbers yet—just the big picture! This technique shows the examiner you understand the overall “story” of the data, which is essential for Band 7+.
A strong overview summarises the main trends, not details, for a Band 7+. The writer points out increases and decreases and makes a comparison between countries. No specific numbers yet—just the big picture! This technique shows the examiner you understand the overall “story” of the data, which is essential for Band 7+.
3
Body Paragraph 1: Recycling Data & Comparisons
(Show/Hide)
In 2015, Germany recycled the largest proportion of waste (62%), followed by the UK (45%) and Italy (31%). By 2025, recycling rates are expected to rise in all countries, with Germany increasing to 70%, the UK to 58%, and Italy to 45%.
Explanation:
This paragraph groups and compares data for a single category (“recycled”). It uses precise percentages, shows clear progression, and directly compares countries and years. The passive structure (“are expected to rise”) and varied language demonstrate a Band 8–9 style. All figures are carefully referenced.
This paragraph groups and compares data for a single category (“recycled”). It uses precise percentages, shows clear progression, and directly compares countries and years. The passive structure (“are expected to rise”) and varied language demonstrate a Band 8–9 style. All figures are carefully referenced.
4
Body Paragraph 2: Landfilling & Incineration
(Show/Hide)
Landfilling was most common in Italy in 2015 (53%), but is projected to fall to 38% by 2025. The UK also reduces its landfill share from 38% to 27%, while Germany’s figure drops from 25% to 18%. Incineration, meanwhile, remains comparatively stable in all three countries, with only minor decreases by 2025.
Explanation:
The writer groups the next two categories, describes changes, and uses a range of comparative and passive forms (“was most common,” “is projected to fall”). The language is concise and the logic is clear. Grouping by method rather than by country is a Band 8+ skill.
The writer groups the next two categories, describes changes, and uses a range of comparative and passive forms (“was most common,” “is projected to fall”). The language is concise and the logic is clear. Grouping by method rather than by country is a Band 8+ skill.
5
Final Summary & Key Comparisons
(Show/Hide)
To summarise, recycling is expected to become the dominant form of waste management across all three countries by 2025, especially in Germany. Landfilling is set to decrease, and incineration will remain the least-used method overall.
Explanation:
The conclusion reinforces the overall trends with high-level comparative language and a final, analytical statement. This kind of synthesis (instead of simple repetition) is crucial for Band 8–9. Avoid personal opinions and keep focus on the data.
The conclusion reinforces the overall trends with high-level comparative language and a final, analytical statement. This kind of synthesis (instead of simple repetition) is crucial for Band 8–9. Avoid personal opinions and keep focus on the data.
Test Yourself: Band 9 Answer Key Quiz
Choose the best answer for each analysis question about the model response. Instantly see a full explanation for each choice!
20 Crucial Words for This IELTS Task
Master these high-impact vocabulary items from the model answer and chart. Tap/click each word for a deep explanation, example, and common mistakes!
proportion ▼
Phonetics: /prəˈpɔː.ʃən/ (BrE), /prəˈpɔr.ʃən/ (AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: proportion of X; a (large/small) proportion
Definition: The part or share of a whole, shown as a percentage or fraction.
Example: “A large proportion of waste in Germany was recycled.” (A big share was recycled.)
Common synonym: percentage, share
Common mistakes: Learners confuse “proportion” with “portion” (which means a piece, not a percentage).
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: proportion of X; a (large/small) proportion
Definition: The part or share of a whole, shown as a percentage or fraction.
Example: “A large proportion of waste in Germany was recycled.” (A big share was recycled.)
Common synonym: percentage, share
Common mistakes: Learners confuse “proportion” with “portion” (which means a piece, not a percentage).
projected ▼
Phonetics: /prəˈdʒek.tɪd/ (BrE), /prəˈdʒɛk.tɪd/ (AmE)
Part of speech: adjective (from passive verb)
Pattern: be projected to + verb
Definition: Expected or predicted, based on current trends.
Example: “Recycling is projected to increase by 2025.” (It is expected to rise.)
Common synonym: expected, forecasted
Common mistakes: Students often use “will” instead of the passive “is projected to” in IELTS writing.
Part of speech: adjective (from passive verb)
Pattern: be projected to + verb
Definition: Expected or predicted, based on current trends.
Example: “Recycling is projected to increase by 2025.” (It is expected to rise.)
Common synonym: expected, forecasted
Common mistakes: Students often use “will” instead of the passive “is projected to” in IELTS writing.
decline ▼
Phonetics: /dɪˈklaɪn/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: verb, noun
Pattern: decline in/of; to decline by X%
Definition: To decrease or go down over time.
Example: “Landfilling declined by 15%.” (It dropped.)
Common synonym: decrease, drop
Common mistakes: Using “decline” as an adjective (incorrect); confusing with “refuse” (verb: to say no).
Part of speech: verb, noun
Pattern: decline in/of; to decline by X%
Definition: To decrease or go down over time.
Example: “Landfilling declined by 15%.” (It dropped.)
Common synonym: decrease, drop
Common mistakes: Using “decline” as an adjective (incorrect); confusing with “refuse” (verb: to say no).
category ▼
Phonetics: /ˈkæt.ə.ɡə.ri/ (BrE), /ˈkæt̬.ə.ɡɔː.ri/ (AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: category of X; in the category of
Definition: A group or type of things with shared characteristics.
Example: “Recycling is one category of waste management.” (A type or group.)
Common synonym: type, group
Common mistakes: Misspelling as “catagory.”
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: category of X; in the category of
Definition: A group or type of things with shared characteristics.
Example: “Recycling is one category of waste management.” (A type or group.)
Common synonym: type, group
Common mistakes: Misspelling as “catagory.”
method ▼
Phonetics: /ˈmeθ.əd/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: method of X; a (new) method
Definition: A way of doing something, especially a regular or systematic way.
Example: “Incineration is a method of waste disposal.” (A way to dispose of waste.)
Common synonym: technique, process
Common mistakes: Using “way” for formal writing instead of “method.”
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: method of X; a (new) method
Definition: A way of doing something, especially a regular or systematic way.
Example: “Incineration is a method of waste disposal.” (A way to dispose of waste.)
Common synonym: technique, process
Common mistakes: Using “way” for formal writing instead of “method.”
compare ▼
Phonetics: /kəmˈpeə(r)/ (BrE), /kəmˈper/ (AmE)
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: compare X to/with Y
Definition: To consider similarities and differences between things.
Example: “The charts compare three countries.” (Show similarities/differences.)
Common synonym: contrast (but “contrast” focuses on differences)
Common mistakes: Using “compare” when only talking about one item.
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: compare X to/with Y
Definition: To consider similarities and differences between things.
Example: “The charts compare three countries.” (Show similarities/differences.)
Common synonym: contrast (but “contrast” focuses on differences)
Common mistakes: Using “compare” when only talking about one item.
significant ▼
Phonetics: /sɪɡˈnɪf.ɪ.kənt/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: adjective
Pattern: significant increase/decrease
Definition: Large or important enough to be noticed or to have an effect.
Example: “A significant rise in recycling was observed.” (A large/important increase.)
Common synonym: considerable, substantial
Common mistakes: Using “significative” (incorrect in English).
Part of speech: adjective
Pattern: significant increase/decrease
Definition: Large or important enough to be noticed or to have an effect.
Example: “A significant rise in recycling was observed.” (A large/important increase.)
Common synonym: considerable, substantial
Common mistakes: Using “significative” (incorrect in English).
remain ▼
Phonetics: /rɪˈmeɪn/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: remain + adjective; remain the same
Definition: To continue to be in a particular state.
Example: “Germany remains the leader in recycling.” (It continues to be the leader.)
Common synonym: stay
Common mistakes: Incorrectly using “remind” instead of “remain.”
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: remain + adjective; remain the same
Definition: To continue to be in a particular state.
Example: “Germany remains the leader in recycling.” (It continues to be the leader.)
Common synonym: stay
Common mistakes: Incorrectly using “remind” instead of “remain.”
rate ▼
Phonetics: /reɪt/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: rate of X; recycling rate
Definition: The speed or level of occurrence; often expressed as a percentage.
Example: “The recycling rate increased.” (More waste was recycled.)
Common synonym: percentage, proportion
Common mistakes: Using “ratio” (which means a relationship between two numbers, not a percentage).
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: rate of X; recycling rate
Definition: The speed or level of occurrence; often expressed as a percentage.
Example: “The recycling rate increased.” (More waste was recycled.)
Common synonym: percentage, proportion
Common mistakes: Using “ratio” (which means a relationship between two numbers, not a percentage).
trend ▼
Phonetics: /trend/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: trend in X; upward/downward trend
Definition: A general direction in which something is developing or changing.
Example: “There is an upward trend in recycling.” (It is increasing overall.)
Common synonym: pattern, tendency
Common mistakes: Using “tendency” when meaning “trend” (not always interchangeable).
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: trend in X; upward/downward trend
Definition: A general direction in which something is developing or changing.
Example: “There is an upward trend in recycling.” (It is increasing overall.)
Common synonym: pattern, tendency
Common mistakes: Using “tendency” when meaning “trend” (not always interchangeable).
decline ▼
Phonetics: /dɪˈklaɪn/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun, verb
Pattern: a decline in X
Definition: A reduction in amount or quality.
Example: “There was a decline in landfilling.” (It went down.)
Common synonym: decrease, drop
Common mistakes: Using “decline” for positive trends.
Part of speech: noun, verb
Pattern: a decline in X
Definition: A reduction in amount or quality.
Example: “There was a decline in landfilling.” (It went down.)
Common synonym: decrease, drop
Common mistakes: Using “decline” for positive trends.
dominate ▼
Phonetics: /ˈdɒm.ɪ.neɪt/ (BrE), /ˈdɑː.mə.neɪt/ (AmE)
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: dominate X; be dominated by
Definition: To be the most important, strongest, or noticeable thing.
Example: “Recycling dominates waste management in Germany.” (It is the most common.)
Common synonym: lead, prevail
Common mistakes: Using “dominate” with a person as object (not always correct).
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: dominate X; be dominated by
Definition: To be the most important, strongest, or noticeable thing.
Example: “Recycling dominates waste management in Germany.” (It is the most common.)
Common synonym: lead, prevail
Common mistakes: Using “dominate” with a person as object (not always correct).
account for ▼
Phonetics: /əˈkaʊnt fə(r)/ (BrE), /əˈkaʊnt fər/ (AmE)
Part of speech: phrasal verb
Pattern: account for X%
Definition: To make up or form a specific part of something.
Example: “Recycling accounted for 62% of waste in Germany.” (It was 62%.)
Common synonym: represent
Common mistakes: Using “explain” (it doesn’t mean “explain” here).
Part of speech: phrasal verb
Pattern: account for X%
Definition: To make up or form a specific part of something.
Example: “Recycling accounted for 62% of waste in Germany.” (It was 62%.)
Common synonym: represent
Common mistakes: Using “explain” (it doesn’t mean “explain” here).
overall ▼
Phonetics: /ˌəʊ.vərˈɔːl/ (BrE), /ˌoʊ.vɚˈɑːl/ (AmE)
Part of speech: adverb, adjective
Pattern: overall, ...; the overall trend
Definition: Considering or including everything.
Example: “Overall, recycling is expected to rise.” (In general, recycling increases.)
Common synonym: in general
Common mistakes: Using “overall” at the end of sentences (unnatural).
Part of speech: adverb, adjective
Pattern: overall, ...; the overall trend
Definition: Considering or including everything.
Example: “Overall, recycling is expected to rise.” (In general, recycling increases.)
Common synonym: in general
Common mistakes: Using “overall” at the end of sentences (unnatural).
respectively ▼
Phonetics: /rɪˈspek.tɪv.li/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: adverb
Pattern: X and Y, respectively
Definition: Referring to two or more items in the order they were mentioned.
Example: “Italy and Germany recycled 31% and 62%, respectively.” (Italy: 31%, Germany: 62%.)
Common synonym: in turn
Common mistakes: Using “respectively” to refer to only one item.
Part of speech: adverb
Pattern: X and Y, respectively
Definition: Referring to two or more items in the order they were mentioned.
Example: “Italy and Germany recycled 31% and 62%, respectively.” (Italy: 31%, Germany: 62%.)
Common synonym: in turn
Common mistakes: Using “respectively” to refer to only one item.
increase ▼
Phonetics: /ɪnˈkriːs/ (verb), /ˈɪn.kriːs/ (noun)
Part of speech: verb, noun
Pattern: increase in; to increase by X%
Definition: To become greater in number or amount.
Example: “There was an increase in recycling rates.” (Recycling rose.)
Common synonym: rise, growth
Common mistakes: Spelling confusion between verb/noun forms.
Part of speech: verb, noun
Pattern: increase in; to increase by X%
Definition: To become greater in number or amount.
Example: “There was an increase in recycling rates.” (Recycling rose.)
Common synonym: rise, growth
Common mistakes: Spelling confusion between verb/noun forms.
contrast ▼
Phonetics: /ˈkɒn.trɑːst/ (BrE noun), /kənˈtræst/ (AmE verb)
Part of speech: verb, noun
Pattern: contrast X with Y
Definition: To show or express the differences between things.
Example: “The data contrasts Germany and the UK.” (Shows differences.)
Common synonym: differ, distinguish
Common mistakes: Using “contrast” as a synonym for “compare” (it means to focus only on differences).
Part of speech: verb, noun
Pattern: contrast X with Y
Definition: To show or express the differences between things.
Example: “The data contrasts Germany and the UK.” (Shows differences.)
Common synonym: differ, distinguish
Common mistakes: Using “contrast” as a synonym for “compare” (it means to focus only on differences).
stability ▼
Phonetics: /stəˈbɪl.ɪ.ti/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: stability of X; remain stable
Definition: The state of being steady and not changing.
Example: “Incineration rates showed stability.” (They stayed the same.)
Common synonym: steadiness
Common mistakes: Using “stability” as an adjective (should use “stable”).
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: stability of X; remain stable
Definition: The state of being steady and not changing.
Example: “Incineration rates showed stability.” (They stayed the same.)
Common synonym: steadiness
Common mistakes: Using “stability” as an adjective (should use “stable”).
fluctuate ▼
Phonetics: /ˈflʌk.tʃu.eɪt/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: fluctuate between X and Y; to fluctuate over time
Definition: To change frequently, especially from one extreme to another.
Example: “Incineration rates fluctuated slightly.” (They changed a little.)
Common synonym: vary
Common mistakes: Writing “fluctuate” for steady or one-way changes.
Part of speech: verb
Pattern: fluctuate between X and Y; to fluctuate over time
Definition: To change frequently, especially from one extreme to another.
Example: “Incineration rates fluctuated slightly.” (They changed a little.)
Common synonym: vary
Common mistakes: Writing “fluctuate” for steady or one-way changes.
analysis ▼
Phonetics: /əˈnæl.ə.sɪs/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: analysis of X; in-depth analysis
Definition: Careful study of something to learn about its parts, causes, or results.
Example: “The analysis showed clear trends.” (The careful study showed trends.)
Common synonym: study, examination
Common mistakes: Using “analysis” as a verb (should be “analyse”).
Part of speech: noun
Pattern: analysis of X; in-depth analysis
Definition: Careful study of something to learn about its parts, causes, or results.
Example: “The analysis showed clear trends.” (The careful study showed trends.)
Common synonym: study, examination
Common mistakes: Using “analysis” as a verb (should be “analyse”).
20 Crucial Phrases & Expressions for IELTS Task 1
Learn and master the most useful expressions for describing, comparing, and analysing data. Tap/click each phrase for details and usage notes!
the largest proportion of ▼
Phonetics: /ðə ˈlɑː.dʒɪst prəˈpɔː.ʃən ɒv/ (BrE), /ðə ˈlɑːr.dʒəst prəˈpɔr.ʃən ʌv/ (AmE)
Part of speech: noun phrase
Pattern: the largest proportion of + noun
Definition: The biggest part or share of something compared to the whole.
Example: “Germany recycled the largest proportion of waste.” (Germany recycled the most.)
Common synonym: highest percentage
Common mistakes: Saying “the most proportion” (incorrect).
Part of speech: noun phrase
Pattern: the largest proportion of + noun
Definition: The biggest part or share of something compared to the whole.
Example: “Germany recycled the largest proportion of waste.” (Germany recycled the most.)
Common synonym: highest percentage
Common mistakes: Saying “the most proportion” (incorrect).
by contrast ▼
Phonetics: /baɪ ˈkɒn.trɑːst/ (BrE), /baɪ ˈkɑːn.træst/ (AmE)
Part of speech: linking phrase/adverb
Pattern: Sentence A. By contrast, sentence B.
Definition: Used to highlight a difference between two things.
Example: “Germany recycled 62%. By contrast, Italy recycled only 31%.” (Shows the difference.)
Common synonym: in comparison
Common mistakes: Using “in contrast by” (incorrect).
Part of speech: linking phrase/adverb
Pattern: Sentence A. By contrast, sentence B.
Definition: Used to highlight a difference between two things.
Example: “Germany recycled 62%. By contrast, Italy recycled only 31%.” (Shows the difference.)
Common synonym: in comparison
Common mistakes: Using “in contrast by” (incorrect).
is projected to ▼
Phonetics: /ɪz prəˈdʒek.tɪd tuː/ (BrE), /ɪz prəˈdʒɛk.tɪd tuː/ (AmE)
Part of speech: passive verb phrase
Pattern: is projected to + base verb
Definition: Expected to happen in the future according to data or trends.
Example: “Landfilling is projected to decrease.” (It is expected to go down.)
Common synonym: is expected to
Common mistakes: Using “will” instead of this passive structure in academic writing.
Part of speech: passive verb phrase
Pattern: is projected to + base verb
Definition: Expected to happen in the future according to data or trends.
Example: “Landfilling is projected to decrease.” (It is expected to go down.)
Common synonym: is expected to
Common mistakes: Using “will” instead of this passive structure in academic writing.
remains the leader ▼
Phonetics: /rɪˈmeɪnz ðə ˈliː.dər/ (BrE), /rɪˈmeɪnz ðə ˈliː.dɚ/ (AmE)
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: X remains the leader (in Y)
Definition: Continues to be in first position or most successful.
Example: “Germany remains the leader in recycling.” (Still first place.)
Common synonym: continues to lead
Common mistakes: Using “reminds” instead of “remains.”
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: X remains the leader (in Y)
Definition: Continues to be in first position or most successful.
Example: “Germany remains the leader in recycling.” (Still first place.)
Common synonym: continues to lead
Common mistakes: Using “reminds” instead of “remains.”
followed by ▼
Phonetics: /ˈfɒl.əʊd baɪ/ (BrE), /ˈfɑː.ləʊd baɪ/ (AmE)
Part of speech: passive verb phrase
Pattern: X, followed by Y
Definition: Something comes next in a list or sequence.
Example: “Germany was followed by the UK.” (The UK was next after Germany.)
Common synonym: next comes
Common mistakes: Writing “was follow by” (incorrect tense).
Part of speech: passive verb phrase
Pattern: X, followed by Y
Definition: Something comes next in a list or sequence.
Example: “Germany was followed by the UK.” (The UK was next after Germany.)
Common synonym: next comes
Common mistakes: Writing “was follow by” (incorrect tense).
accounted for ▼
Phonetics: /əˈkaʊntɪd fɔː(r)/ (BrE), /əˈkaʊntɪd fɔːr/ (AmE)
Part of speech: phrasal verb (past tense)
Pattern: accounted for + number/percentage
Definition: Made up or formed part of something.
Example: “Recycling accounted for 62% of waste.” (It made up 62%.)
Common synonym: made up
Common mistakes: Using “explained” for data (wrong meaning).
Part of speech: phrasal verb (past tense)
Pattern: accounted for + number/percentage
Definition: Made up or formed part of something.
Example: “Recycling accounted for 62% of waste.” (It made up 62%.)
Common synonym: made up
Common mistakes: Using “explained” for data (wrong meaning).
there was a decline in ▼
Phonetics: /ðeə wɒz ə dɪˈklaɪn ɪn/ (BrE), /ðer wʌz ə dɪˈklaɪn ɪn/ (AmE)
Part of speech: fixed phrase
Pattern: there was a decline in + noun
Definition: Something decreased or fell in amount.
Example: “There was a decline in landfilling.” (Landfilling went down.)
Common synonym: decrease in
Common mistakes: Using “decline of” incorrectly (“decline in” for amount).
Part of speech: fixed phrase
Pattern: there was a decline in + noun
Definition: Something decreased or fell in amount.
Example: “There was a decline in landfilling.” (Landfilling went down.)
Common synonym: decrease in
Common mistakes: Using “decline of” incorrectly (“decline in” for amount).
respectively ▼
Phonetics: /rɪˈspek.tɪv.li/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: adverb
Pattern: X and Y, respectively
Definition: In the order given.
Example: “UK and Italy recycled 58% and 45%, respectively.” (UK: 58%, Italy: 45%.)
Common synonym: in that order
Common mistakes: Using with only one item.
Part of speech: adverb
Pattern: X and Y, respectively
Definition: In the order given.
Example: “UK and Italy recycled 58% and 45%, respectively.” (UK: 58%, Italy: 45%.)
Common synonym: in that order
Common mistakes: Using with only one item.
it is expected that ▼
Phonetics: /ɪt ɪz ɪkˈspek.tɪd ðæt/ (BrE), /ɪt ɪz ɪkˈspek.tɪd ðæt/ (AmE)
Part of speech: impersonal passive phrase
Pattern: it is expected that + clause
Definition: People believe something will happen in the future.
Example: “It is expected that recycling rates will increase.” (People think rates will rise.)
Common synonym: is projected to
Common mistakes: Using “is hope that” (should be “is expected that”).
Part of speech: impersonal passive phrase
Pattern: it is expected that + clause
Definition: People believe something will happen in the future.
Example: “It is expected that recycling rates will increase.” (People think rates will rise.)
Common synonym: is projected to
Common mistakes: Using “is hope that” (should be “is expected that”).
make comparisons ▼
Phonetics: /meɪk kəmˈpær.ɪ.sənz/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: make comparisons between X and Y
Definition: To point out similarities and differences.
Example: “You should make comparisons between countries.” (Show similarities/differences.)
Common synonym: compare
Common mistakes: Forgetting to use “between.”
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: make comparisons between X and Y
Definition: To point out similarities and differences.
Example: “You should make comparisons between countries.” (Show similarities/differences.)
Common synonym: compare
Common mistakes: Forgetting to use “between.”
by 2025 ▼
Phonetics: /baɪ ˌtwɛnti ˈtwɛnti faɪv/
Part of speech: time prepositional phrase
Pattern: by + year
Definition: No later than the stated year.
Example: “Recycling will increase by 2025.” (Before or at 2025.)
Common synonym: before 2025
Common mistakes: Using “in 2025” when “by 2025” is meant.
Part of speech: time prepositional phrase
Pattern: by + year
Definition: No later than the stated year.
Example: “Recycling will increase by 2025.” (Before or at 2025.)
Common synonym: before 2025
Common mistakes: Using “in 2025” when “by 2025” is meant.
remained stable ▼
Phonetics: /rɪˈmeɪnd ˈsteɪ.bəl/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: remained stable over (period)
Definition: Did not change much over time.
Example: “Incineration remained stable.” (It stayed about the same.)
Common synonym: was steady
Common mistakes: Using “stable” as a verb.
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: remained stable over (period)
Definition: Did not change much over time.
Example: “Incineration remained stable.” (It stayed about the same.)
Common synonym: was steady
Common mistakes: Using “stable” as a verb.
there was a rise in ▼
Phonetics: /ðeə wɒz ə raɪz ɪn/ (BrE), /ðer wʌz ə raɪz ɪn/ (AmE)
Part of speech: fixed phrase
Pattern: there was a rise in + noun
Definition: Something increased.
Example: “There was a rise in recycling.” (Recycling went up.)
Common synonym: increase in
Common mistakes: Using “rise of” instead of “rise in.”
Part of speech: fixed phrase
Pattern: there was a rise in + noun
Definition: Something increased.
Example: “There was a rise in recycling.” (Recycling went up.)
Common synonym: increase in
Common mistakes: Using “rise of” instead of “rise in.”
in terms of ▼
Phonetics: /ɪn tɜːmz ɒv/ (BrE), /ɪn tɝːmz ʌv/ (AmE)
Part of speech: prepositional phrase
Pattern: in terms of + noun
Definition: With regard to; concerning.
Example: “Germany leads in terms of recycling.” (Regarding recycling, Germany is first.)
Common synonym: regarding, concerning
Common mistakes: Using “in the term of” (incorrect).
Part of speech: prepositional phrase
Pattern: in terms of + noun
Definition: With regard to; concerning.
Example: “Germany leads in terms of recycling.” (Regarding recycling, Germany is first.)
Common synonym: regarding, concerning
Common mistakes: Using “in the term of” (incorrect).
in all three countries ▼
Phonetics: /ɪn ɔːl θriː ˈkʌn.triz/ (BrE), /ɪn ɔːl θriː ˈkʌn.triz/ (AmE)
Part of speech: prepositional phrase
Pattern: in all three countries
Definition: Referring to every country mentioned.
Example: “Recycling increased in all three countries.” (Every country mentioned saw an increase.)
Common synonym: in each country
Common mistakes: Using “in all of three countries” (incorrect).
Part of speech: prepositional phrase
Pattern: in all three countries
Definition: Referring to every country mentioned.
Example: “Recycling increased in all three countries.” (Every country mentioned saw an increase.)
Common synonym: in each country
Common mistakes: Using “in all of three countries” (incorrect).
the least-used method ▼
Phonetics: /ðə liːst juːzd ˈmeθ.əd/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: noun phrase
Pattern: the least-used method
Definition: The method used the smallest number of times.
Example: “Incineration was the least-used method.” (Used the least.)
Common synonym: least common method
Common mistakes: Writing “less used method” (incorrect comparative).
Part of speech: noun phrase
Pattern: the least-used method
Definition: The method used the smallest number of times.
Example: “Incineration was the least-used method.” (Used the least.)
Common synonym: least common method
Common mistakes: Writing “less used method” (incorrect comparative).
in comparison to ▼
Phonetics: /ɪn kəmˈpær.ɪ.sən tuː/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: prepositional phrase
Pattern: in comparison to/with + noun
Definition: Used to show differences or similarities.
Example: “Germany recycled more in comparison to Italy.”
Common synonym: compared with
Common mistakes: Mixing up “to” and “with.”
Part of speech: prepositional phrase
Pattern: in comparison to/with + noun
Definition: Used to show differences or similarities.
Example: “Germany recycled more in comparison to Italy.”
Common synonym: compared with
Common mistakes: Mixing up “to” and “with.”
was most common in ▼
Phonetics: /wɒz məʊst ˈkɒm.ən ɪn/ (BrE), /wəz moʊst ˈkɑː.mən ɪn/ (AmE)
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: was most common in + noun
Definition: Happened the most in a particular place/time.
Example: “Landfilling was most common in Italy.”
Common synonym: occurred most in
Common mistakes: Writing “was the most common in” (sometimes redundant).
Part of speech: verb phrase
Pattern: was most common in + noun
Definition: Happened the most in a particular place/time.
Example: “Landfilling was most common in Italy.”
Common synonym: occurred most in
Common mistakes: Writing “was the most common in” (sometimes redundant).
is set to ▼
Phonetics: /ɪz set tuː/ (BrE & AmE)
Part of speech: passive/modal phrase
Pattern: is set to + base verb
Definition: Is expected to happen in the near future.
Example: “Landfilling is set to decrease.”
Common synonym: is projected to
Common mistakes: Using “is setting to” (incorrect).
Part of speech: passive/modal phrase
Pattern: is set to + base verb
Definition: Is expected to happen in the near future.
Example: “Landfilling is set to decrease.”
Common synonym: is projected to
Common mistakes: Using “is setting to” (incorrect).
to summarise ▼
Phonetics: /tə ˈsʌm.ə.raɪz/ (BrE), /tə ˈsʌm.ə.raɪz/ (AmE)
Part of speech: phrase (verb)
Pattern: To summarise, ...
Definition: Used to signal a brief, clear restatement of main points.
Example: “To summarise, recycling increased everywhere.”
Common synonym: in conclusion
Common mistakes: Using “to summarize” (spelling difference UK/US).
Part of speech: phrase (verb)
Pattern: To summarise, ...
Definition: Used to signal a brief, clear restatement of main points.
Example: “To summarise, recycling increased everywhere.”
Common synonym: in conclusion
Common mistakes: Using “to summarize” (spelling difference UK/US).
Interactive Exercise 1: Vocabulary & Phrases Practice
Test your mastery of the most important words and expressions from this IELTS Writing Task 1! Select the correct answer. Get an instant explanation after every choice.
Interactive Exercise 2: Phrases & Expressions in Context
Practise using the most important IELTS Task 1 phrases. Read the sentence and choose the answer that fits best in context. Instantly view a deep explanation for every answer!
You May Also Like
-
Sep 25, 2025
Step-by-step IELTS Task 2 tutorial on the Causes & Solutions essay: template, Band 6–8 sample answers, 10 key words &...
-
Sep 25, 2025
Step-by-step IELTS Task 2 tutorial on the Causes & Solutions essay: template, Band 6–8 sample answers, 10 key words &...
-
Sep 25, 2025
Master IELTS Academic Writing Task 2 on air pollution with a step-by-step causes–solutions tutorial, fill-in template, timer, Band 6–8 sample...
-
Sep 25, 2025
Master IELTS Task 2 “outweigh” essays on the working-from-home topic with a step-by-step tutorial, fill-in template, timer, Band 6–8 samples,...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
Get in touch
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
info@lingexam.com
Need some help?
My Notes
✓ Notes copied to clipboard!
×
Book Your Free Consultation
Welcome


Stay Connected & Boost Your IELTS Progress!